Noisy Entanglement (on Color Centers)
Stefan Krastanov | MITEntanglement


They can be entangled!
\[\begin{aligned}
A=|\phi_{+}\rangle=\frac{|00\rangle+|11\rangle}{\sqrt{2}}\\
B=|\psi_{-}\rangle=\frac{|01\rangle-|10\rangle}{\sqrt{2}}\\
C=|\psi_{+}\rangle=\frac{|01\rangle+|10\rangle}{\sqrt{2}}\\
D=|\phi_{-}\rangle=\frac{|00\rangle-|11\rangle}{\sqrt{2}}
\end{aligned}\]

They can be entangled!
\[\begin{aligned}
A=|\phi_{+}\rangle=\frac{|00\rangle+|11\rangle}{\sqrt{2}}\\
B=|\psi_{-}\rangle=\frac{|01\rangle-|10\rangle}{\sqrt{2}}\\
C=|\psi_{+}\rangle=\frac{|01\rangle+|10\rangle}{\sqrt{2}}\\
D=|\phi_{-}\rangle=\frac{|00\rangle-|11\rangle}{\sqrt{2}}
\end{aligned}\]
- Krastanov et al.Art installation on Non-contextual Hidden Variable theories
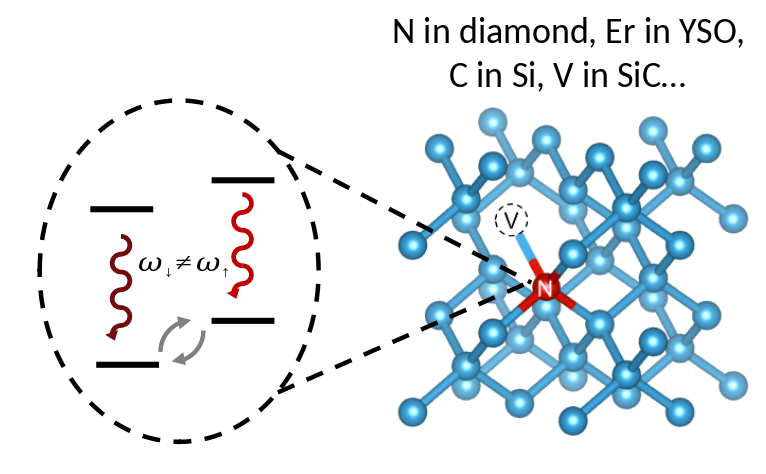
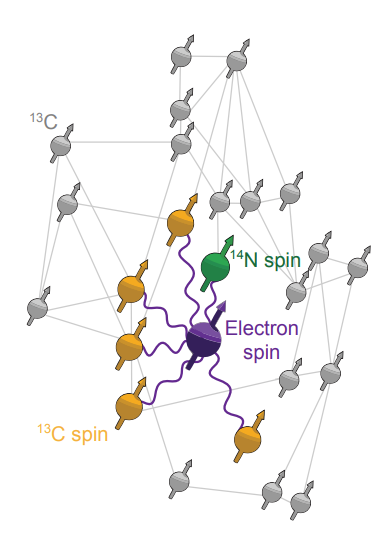
Entanglement with Color Centers
The Color Center
Entanglement Protocols
Inherently low probability of success (DLCZ-like)
Full excitation and path erasure (Barret-Kok)
Single-photon reflection
Atom-photon gates (Duan-Kimble)
Low-probability of success codes (DLCZ-like)



Full excitation and path erasure (Barret-Kok)

Single-photon reflection

Atom-photon gates (Duan-Kimble)

| Rate | only classical light | no optical excitation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DLCZ | \( \eta (1-F) \) | ✅ | ❌ |
| BK | \( \eta^2 \) | ✅ | ❌ |
| reflection | \( \eta^2 \) | ❌ | ✅ |
You also need a color center that does not suffer from spectral diffusion or charge state instabilities.
If you end up with significant optical excitation, you also need a way to turn off the hyperfine coupling to the (nuclear) memory.
First Steps to Entanglement Purification
They can be noisy!
Desired:
\[\begin{aligned} A=\frac{|00\rangle+|11\rangle}{\sqrt{2}}\\ \end{aligned}\]The hardware generated:
90% chance for \[\begin{aligned} A=\frac{|00\rangle+|11\rangle}{\sqrt{2}}\\ \end{aligned}\] 10% chance for a bit flip on Bob's qubit \[\begin{aligned} C=\frac{|01\rangle+|10\rangle}{\sqrt{2}}\\ \end{aligned}\]Purification of entanglement
\[\begin{aligned}
A=|\phi_{+}\rangle=\frac{|00\rangle+|11\rangle}{\sqrt{2}}\\
B=|\psi_{-}\rangle=\frac{|01\rangle-|10\rangle}{\sqrt{2}}\\
C=|\psi_{+}\rangle=\frac{|01\rangle+|10\rangle}{\sqrt{2}}\\
D=|\phi_{-}\rangle=\frac{|00\rangle-|11\rangle}{\sqrt{2}}
\end{aligned}\]
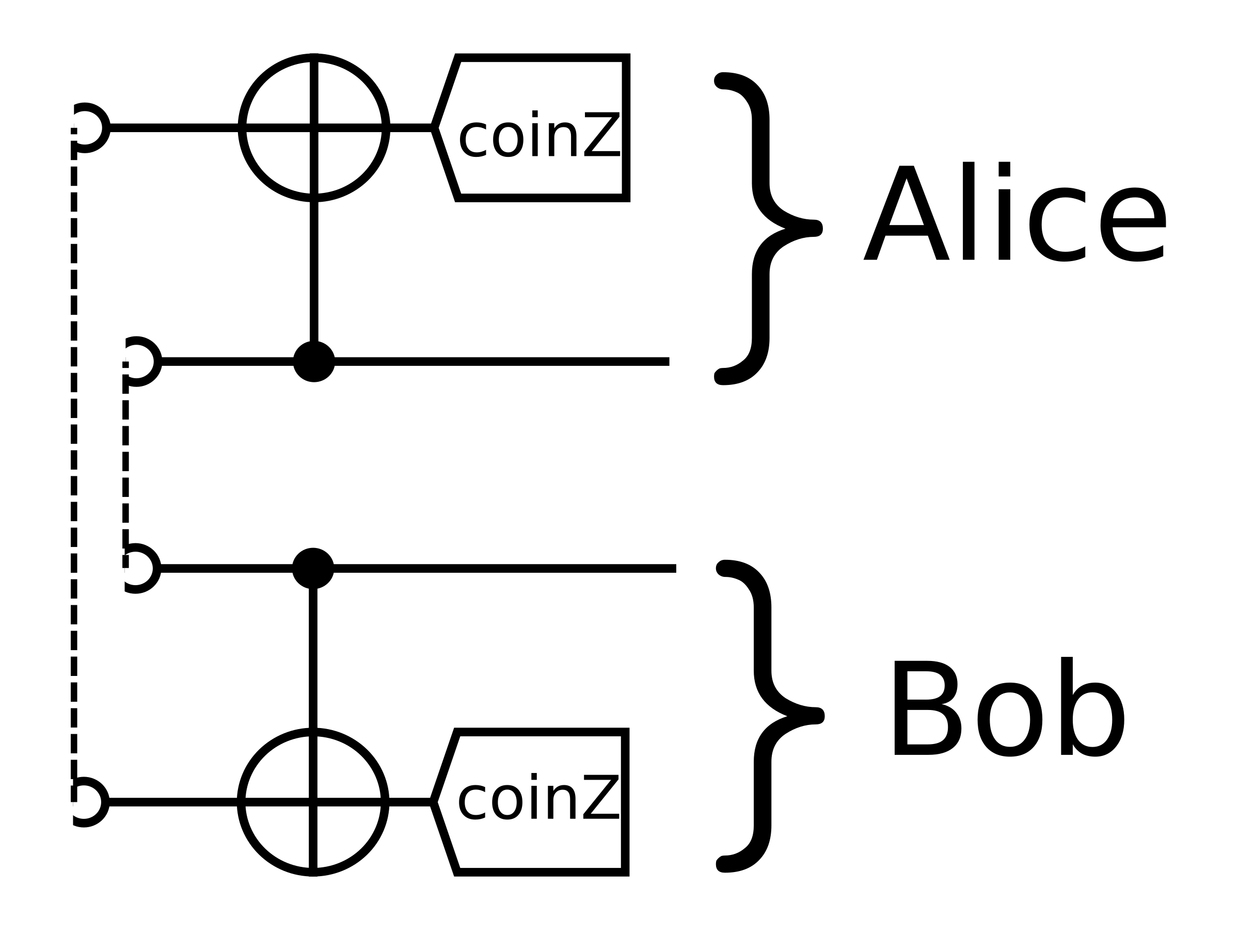
\[\begin{aligned}
A\propto|00\rangle+|11\rangle\\
B\propto|01\rangle-|10\rangle\\
C\propto|01\rangle+|10\rangle\\
D\propto|00\rangle-|11\rangle
\end{aligned}\]


\[\begin{aligned}
A\propto|00\rangle+|11\rangle\\
B\propto|01\rangle-|10\rangle\\
C\propto|01\rangle+|10\rangle\\
D\propto|00\rangle-|11\rangle
\end{aligned}\]

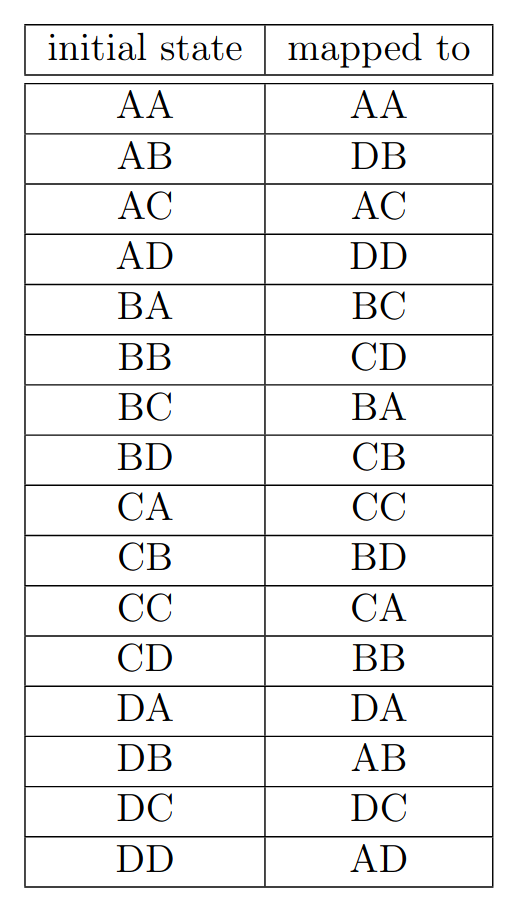
\[\begin{aligned}
A\propto|00\rangle+|11\rangle\\
B\propto|01\rangle-|10\rangle\\
C\propto|01\rangle+|10\rangle\\
D\propto|00\rangle-|11\rangle
\end{aligned}\]



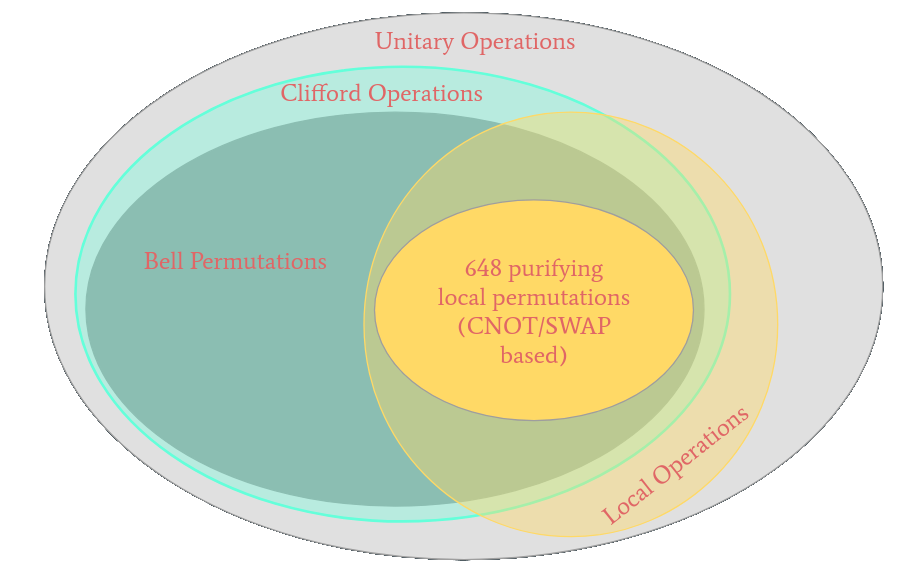
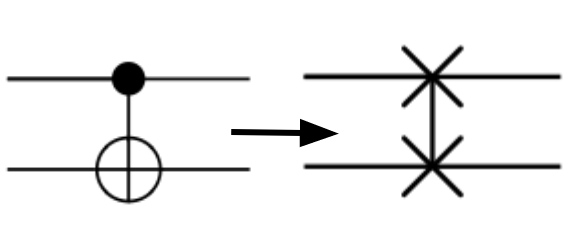
What if we want multi-sacrifice circuit?
Discrete Optimization: Evolutionary Algorithm
Discrete Optimization: Evolutionary Algorithm
Discrete Optimization: Evolutionary Algorithm

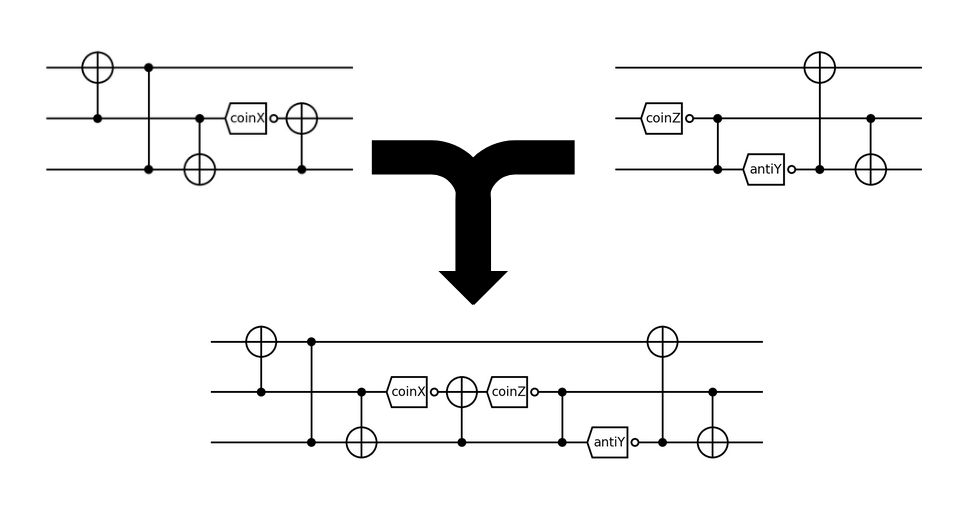

(c) resource usage for each
- Krastanov et al.Optimized Entanglement Purification
- Krastanov et al.Optimized Entanglement Purification

- Krastanov et al.Optimized Entanglement Purification
Circuit Constraints

Ongoing projects and useful tools
Faster purificaiton simulators¹
n-to-k purification circuits²
Rigorous theory bounds on purification performance³
QuantumClifford.jl and QuantumSavory.jl
- Shu Ge (an undergrad under advisement)
- Vaishnavi Addala (an undergrad under advisement)
- friends at Delft